Eye injury
An Eye injury can encompass a wide range of conditions that affect the eye or the surrounding area. They can result from various causes such as trauma, foreign objects or chemical exposure. All are serious because they can affect the vision of a casualty.
Emergency Advice ⚠️
If someone has an eye injury:
- Assist the casualty to lay down and support the head.
- Instruct them to keep both eyes still.
- Offer a dressing to cover the eye and secure it.
- Urgently seek medical advice
What is it?
An eye injury is any harm or damage that affects the eye or the surrounding area. These injuries can occur due to various reasons, including accidents, trauma, foreign objects entering the eye, exposure to chemicals or environmental hazards, or underlying medical conditions.
Eye injuries can range from mild irritation caused by small particles like dust or debris to more severe trauma such as corneal abrasions, chemical burns, blunt force trauma, or even penetrating injuries where an object pierces the eye.
Common types of eye injuries include:
- Corneal abrasions: Scratches or cuts on the cornea, often caused by foreign objects or contact lenses.
- Chemical burns: Caused by exposure to harmful chemicals.
- Foreign objects: Particles like dust, metal, or wood entering the eye, causing irritation or damage.
- Blunt force trauma: Injuries resulting from accidents, impacts, or sports-related incidents.
- Penetrating injuries: When a foreign object penetrates the eye, causing internal damage.
The severity of an eye injury can vary, and while some may cause temporary discomfort, others can lead to serious vision problems or permanent damage. Immediate care and appropriate treatment are essential to prevent long-term complications and preserve vision.
Recognition features
Signs and symptoms
Keep an eye out for 😏:
- Eye or eyelid discomfort.
- Evident injury or redness.
- Embedded objects.
- Partial or complete vision impairment.
- Release of blood or clear fluid from an injury.
Treatment
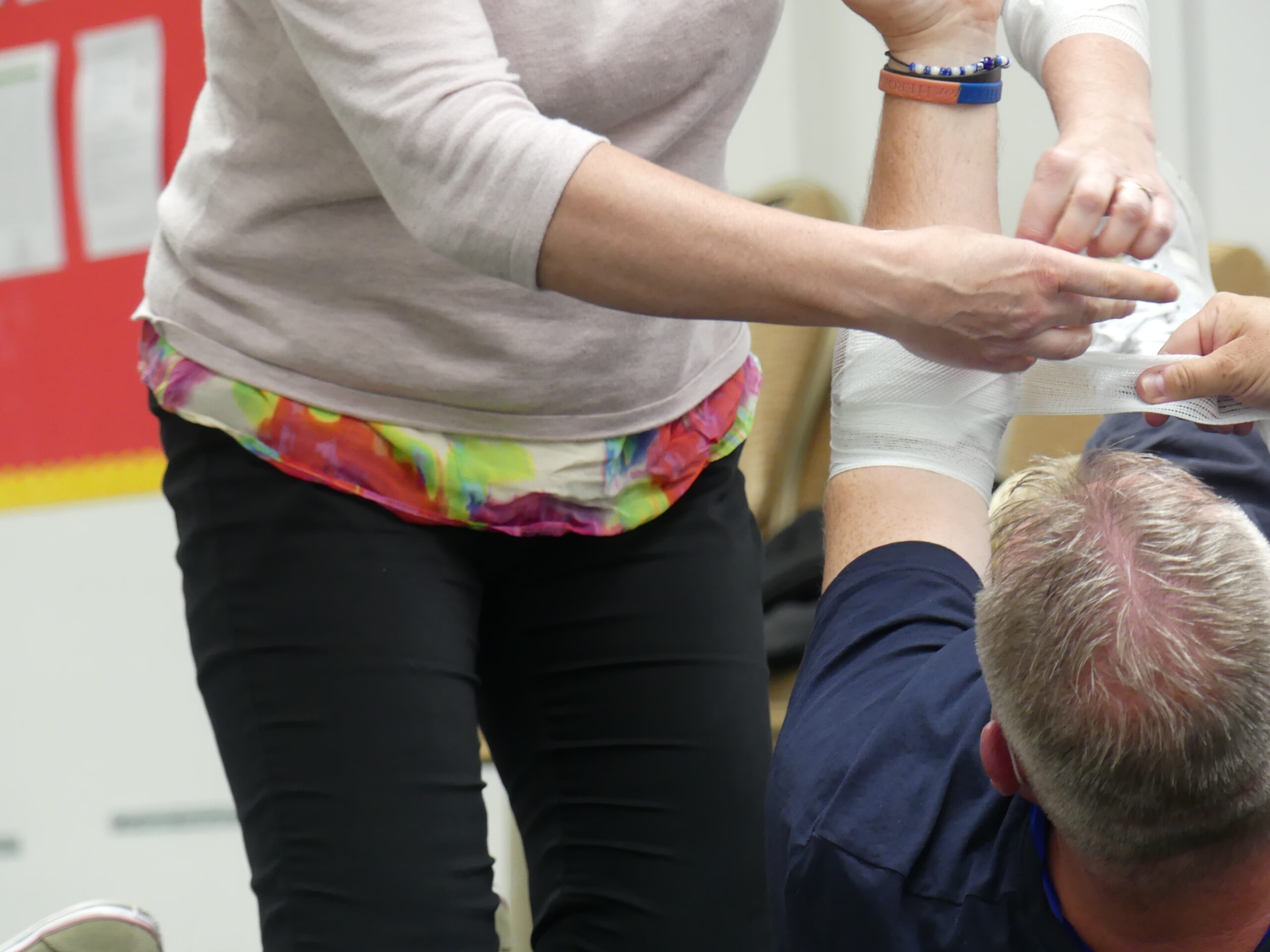
Eye Wound
- Assist the injured person in lying on their back while supporting their head to minimize movement.
Advise them to keep both eyes still, as movement in the unaffected eye might cause further harm to the injured one because they move together.
- Provide a sterile or clean, non-fluffy pad to cover the affected eye gently and secure it in position using a bandage.
- Seek immediate medical advice.
Foreign object in the eye e.g. dust, dirt, grit
- Gloves on!
Wear gloves or wash hands thoroughly to ensure cleanliness before dealing with the affected eye.
- Don’t rub it!
Advise the person not to rub the eye, as it may worsen the irritation or embed the particle deeper.
- Examine the eye
Ask the to casualty to hold their eye open (you may need to do this for them) and examine for particles
- Flush
Gently flush the eye with clean, lukewarm water or saline solution from your first aid kit, tilting the head to the affected side to allow the water to flow over the eye and out.
- Moist swab
If the particle remains, consider using a clean, damp cloth or gauze to gently remove visible particles on the white of the eye or eyelid.
- Seek medical advice
If the particle persists, causes intense pain, impaired vision, or persistent discomfort, seek medical assistance promptly.
Train with us
This subject is covered in detail on the following courses that we offer:
- First Aid at Work
- Paediatric First Aid
- First Aid at Work Requalification
- Combined First Aid at Work and Paediatric First Aid
Be prepared for anything with our first aid supplies 👀
-
 Universal First Aid Kit£15.00
Universal First Aid Kit£15.00 -
 First Aid Kit – Refill£7.95
First Aid Kit – Refill£7.95 -
 CPR Face Shield Key Ring£3.50
CPR Face Shield Key Ring£3.50